Explain Different Types of Crystal Structure
Binary crystals are composed of two elements. The MONOCLINIC system 6.

Chemistry Liquids And Solids 32 Of 59 Crystal Structure Seven Types Of Unit Cells Youtube
Six-sided prisms with a hexagon cross section.

. Crystal Structure In the above we have discussed the concept of crystal lattice. Closest packing is the most efficient arrangement of spheres. In this system all three axes are inclined to each other.
Crystal structure and its types with examples Types of Lattice Structures. The TRICLINIC system Every Crystal System involves a number of Crystal Classes. In body centered crystal structure one atom is placed at each corner of the.
Hexagonal Close-Packed HCP Crystal Structure. Amorphous Solids They are not rigid so mild effects may change the shape. In this arrangement the constituent lattice points hold the corner positions only.
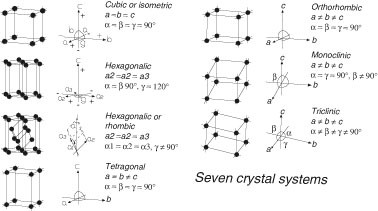
This fourteen space lattice is divided into seven crystal systems. There are many different types but the most common are body-centered cubic BCC iron at low temperature face-centered cubic FCC silver gold and copper and hexagonal closed packed HCP. The TETRAGONAL system 3.
Amorphous Solids Isotropic in nature. These crystals have a three-fold axis. The structure is like a cubic crystal except one axis is longer than the other.
Different types of crystal structures. Face Centred Cubic Crystal Structure 3. The geometry of the unit cell is defined as a parallelepiped providing six lattice parameters taken as the lengths of the cell edges a b c and the angles between them α β γ.
These are rhombic prisms and dipyramids that resemble tetragons but without square cross-sections. The hexagonal crystal system is further broken down into hexagonal and rhombohedral divisions. The unit cell is defined as the smallest repeating unit having the full symmetry of the crystal structure.
Cube diamond fluorite pyrite Octahedron diamond fluorite magnetite Rhombic dodecahedron garnet lapis lazuli rarely crystallises Icosi-tetrahedron pyrite sphalerite Hexacisochedron pyrite. The ORTHORHOMBIC system 5. In addition macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape consisting of flat faces with specific characteristic orientations.
¾Crystal structure can be completely described by specification of a lattice and basis a a Lattice Basis Crystal Structure Lattice is square lattice Basis is large red atom at 00 and small blue atom at ½ a ½ a. There are six Crystal System 1. Body-Centered Crystal Structure BCC.
Crystals can be grown under moderate conditions from all 92 naturally occurring elements except helium and helium can be crystallized at low temperatures by using 25 atmospheres of pressure. A CCP arrangement has a total of 4 spheres per unit cell and an HCP arrangement has 8 spheres per unit cell. This orderly and regular arrangement of the metal balls minimizes the empty space between them.
Simple Cubic Crystal Structure SC. There are seven main structures of crystals depending on the shape of the crystal. Triclinic crystals tend not to be symmetrical.
Octahedral and Tetrahedral Vacancies. Metals are normally crystalline or rather in solid state they are almost synonymous to crystalline state. Every crystal class is a member of one of the six crystal systems.
Hexagonal Close Packing and Cubic Close Packing. Crystal Structures of Metals. The HEXAGONAL system 4.
Specifying Crystal Structure ¾A motif or a basis is a specific arrangement of atoms which belong to a lattice point. The CUBIC also called Isometric system 2. Types of Crystal Systems.
These systems include the isometric hexagonal tetragonal orthorhombic monoclinic and triclinic crystal systems. There are thousands of binary crystals. 1 Diamond structure Fig.
Ie the magnitude of the physical properties is the same along with all directions of the solid. A ball-and-stick model a space-filling cutaway model that shows the portion of each atom that lies within the unit cell and an aggregate of several unit cells. To complete a crystal structure one needs to attach the basis a fixed group of atoms to each lattice point ie Bravais Lattice Basis Crystal Structure Some examples.
For the three kinds of cubic unit cells simple cubic a body-centered cubic b and face-centered cubic c there are three representations for each. Only seven different systems of axis are found to be sufficient to represent all Bravais lattice. However both configurations have a coordination number of 12.
In this article we will discuss about the most common crystal structures in metals- 1. In this type of crystal structure one atom is situated at each corner of the. Based on a square inner structure.
Crystal structure is described in terms of the geometry of arrangement of particles in the unit cell. 38 From Kittel The crystal structure is formed by the. Body Centred Cubic BCC Crystal Structure 2.
The different Crystal Systems. One general triclinic and thirteen special. When identical spheres are stacked each successive layer fits into the small spaces where different spheres come together.
The packing efficiency is the fraction of volume in a crystal structure that is occupied by constituent particles rather than empty space. A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents such as atoms molecules or ions are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. Atoms of a metal crystal are arranged in similar patterns called close.
Some examples are sodium chloride NaCl alumina Al 2 O 3 and ice H 2 O. These are cubic hexagonal tetragonal orthorhombic trigonal. Crystalline Solids They are rigid solids and applying mild forces will not distort its shape.
Description of Crystal Structures. They are triclinic monoclinic orthorhombic tetragonal.

7 1 Crystal Structure Chemistry Libretexts

Crystal Structures Of Metals Chemistry For Non Majors

Chemistry Liquids And Solids 32 Of 59 Crystal Structure Seven Types Of Unit Cells Youtube
0 Response to "Explain Different Types of Crystal Structure"
Post a Comment